Metrology for quantum-based traceability of the pascal
Short Name: MQB-Pascal, Project Number: 22IEM04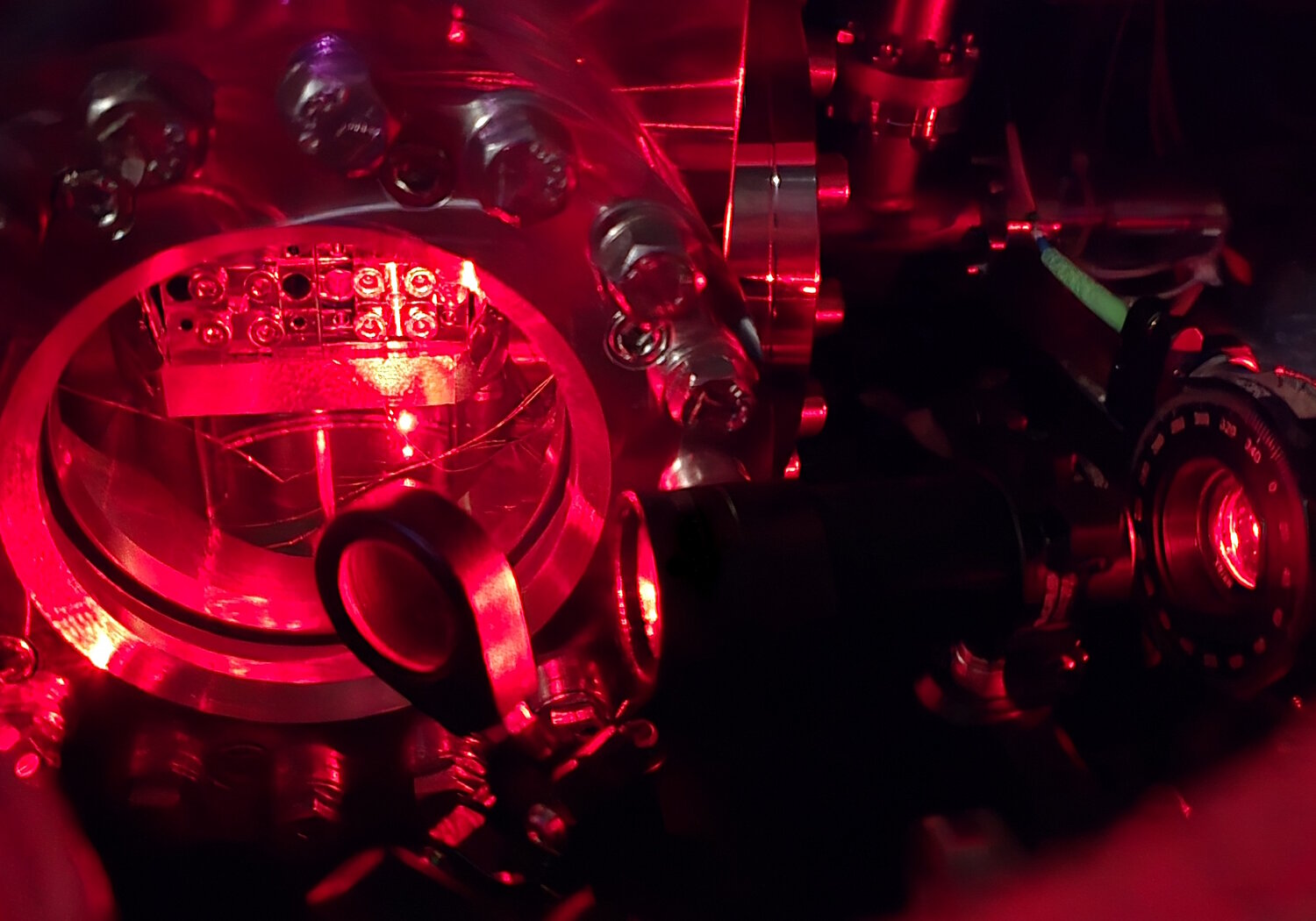
Novel quantum-based technique can help provide faster and more accurate pressure measurements
Many sectors including manufacturing, quality control and medicine require techniques to measure gas pressure in a fast and accurate way. Traditionally, pressure is measured with mercury-containing equipment or piston gauges, where pressure is defined as force over area. However, mercury poses health and environmental hazards and piston gauges require time-consuming calibrations where weights need to be exchanged.
The pascal can also be realised by measuring gas properties such as refractivity or temperature directly, which decreases uncertainties and improves the efficiency of calibration chains. The EMPIR project QuantumPascal worked on establishing calibration-free quantum techniques to measure gas pressure using helium as a reference substance.
However, the uncertainties and metrological reference data need to be improved for applications in industry.
Additionally, most National Metrology Institutes and industries use nitrogen as a reference substance for refractometry measurements, however its metrological reference data is lacking.
This project will develop primary pressure instruments based on Fabry-Perot (FP) refractometry for measurements within the range of 1 Pa to 30 kPa with a target uncertainty of 2 mPa + 10 ppm.
Three fully operational quantum-based primary FP-refractometers will be produced and located in different countries, to ensure that the novel technology is accessible across Europe. The uncertainties of the thermodynamic and electrodynamic properties of nitrogen for a range of temperatures and frequencies will be established. The obtained information will be published in at least 13 open-access papers and presented at relevant conferences.
These advancements will help to implement quantum-based pressure measurement techniques in European industries.
Optics Express
Proceedings of the 7th IMEKO TC16 Conference on Pressure and Vacuum Measurement
Optics Express
Journal of Vacuum Science & Technology B
